In the modern quest for sustainable transportation solutions, hybrid electric cars have emerged as a remarkable innovation. Addressing the pressing concern of environmental impact, these vehicles seamlessly blend traditional internal combustion engines with advanced electric motor technology.
Curious minds often ask, how does a hybrid electric car work? This article explores the mechanics behind these ingenious vehicles, exploring the intricate synergy between gasoline engines and electric motors.
By dissecting the workings of mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid electric cars, we unravel the science that enables them to optimize fuel efficiency, minimize emissions, and provide a glimpse into the future of greener mobility.
Hybrid Electric Cars Overview
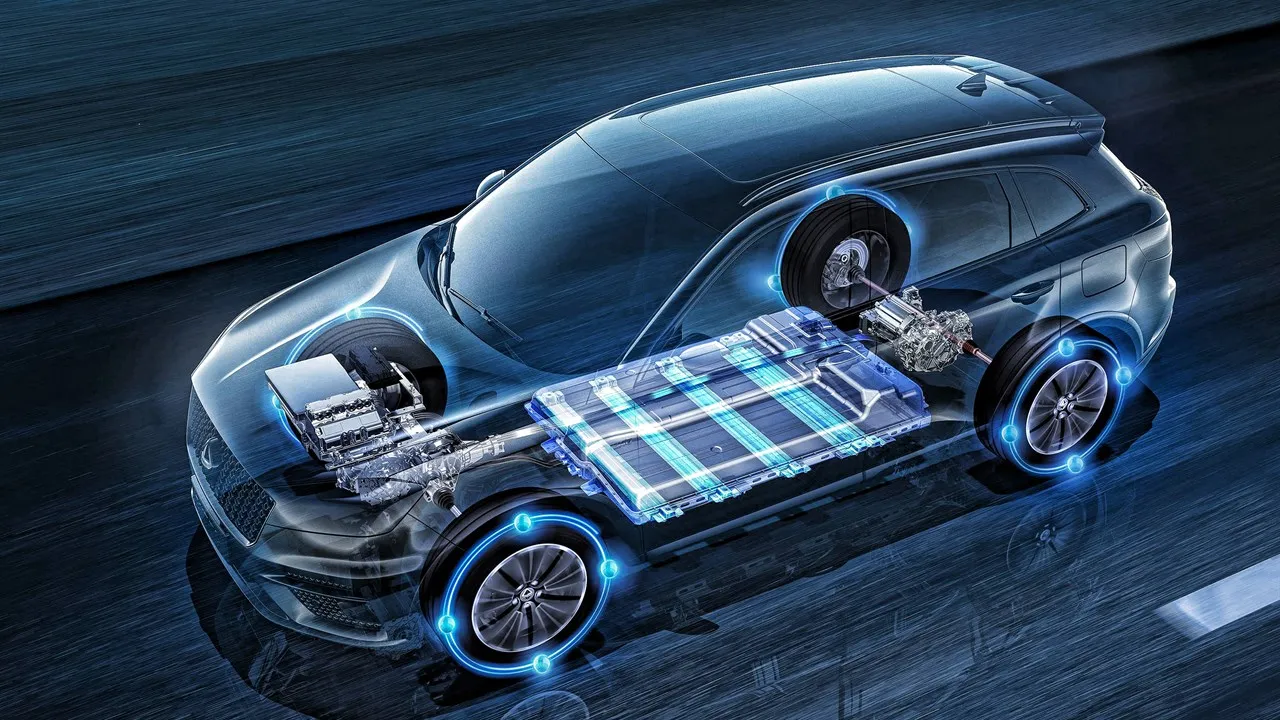
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) operate through a system that utilizes an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. Unlike purely electric cars, hybrids don’t rely solely on batteries for power.
Instead, they combine gasoline and electricity, allowing greater efficiency and reduced emissions. People usually ask, can a hybrid car run on electric only? Mild hybrids can’t run exclusively on electricity; they require the internal combustion engine for primary propulsion.

However, plug-in hybrids can run on electric power alone for a certain distance, determined by battery capacity and driving conditions. This capability makes them ideal for short commutes or city driving.
Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
1) Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicles:
First, let’s get to know how does a mild hybrid electric vehicle work? Mild hybrids incorporate a smaller electric motor that assists the internal combustion engine rather than solely propelling the vehicle.
This motor provides a boost during acceleration, reduces strain on the engine, and enables regenerative braking, converting kinetic energy into stored electricity. However, as mentioned earlier, MHEVs cannot run solely on electric power; the gasoline engine remains essential for driving.
2) Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles:
Now, dig into how does a plug in hybrid electric vehicle works? Plug-in hybrids are equipped with larger battery packs that can be charged through an external power source, such as a charging station.
This enables them to drive longer distances on electricity alone, making them more versatile for urban commutes. When the battery depletes, the internal combustion engine takes over, ensuring the vehicle’s continued operation. PHEVs offer the option to drive entirely on electricity, providing a reduced environmental footprint for short trips.
Hybrid Battery Range and Functionality
How far can a hybrid car go on a battery? This question often piques the curiosity of those exploring the capabilities of plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs). The all-electric range of PHEVs is subject to variations influenced by factors such as battery size and individual driving habits.
Typically, some plug-in hybrids offer an electric travel distance ranging from 20 to 50 miles before the internal combustion engine seamlessly takes over. However, another common query surfaces: what happens if a hybrid battery dies? The response hinges on the type of hybrid in question.
In the case of mild hybrids, where the electric motor plays a supplementary role, the gasoline engine continues to function as it would in a conventional vehicle, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
On the other hand, for plug-in hybrids, if the battery charge depletes, the gasoline engine assumes control. The vehicle then operates similarly to a standard hybrid until the battery is recharged, allowing the dual power sources to maintain a dynamic balance of efficiency and performance.
Hybrid Cars vs Electric Cars
While both hybrids and electric cars contribute to greener transportation, they have distinct characteristics. Let’s look into hybrid car work vs. electric cars:


Power Source:
Hybrid cars combine gasoline engines and electric motors, using both for propulsion. Electric cars rely solely on electricity stored in batteries to power their motors.
Range:
Hybrid cars can switch between gasoline and electricity, providing a longer range than most electric cars. Electric cars’ range depends on battery capacity and typically suits urban travel.
Advantages of Hybrid Cars
Hybrid cars provide compelling advantages that set them apart in modern mobility. Let’s get to know what are 3 advantages of a hybrid car.
1) Improved Fuel Efficiency:
Due to their reliance on electric power during low-speed and stop-and-go driving, hybrids use less fuel than typical petrol cars.
2) Reduced Emissions:
Electric power integration minimizes greenhouse gas emissions and pollutants, promoting cleaner air and environmental sustainability.
3) Regenerative Braking:
Regenerative braking is used in hybrids to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy stored in the battery. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also increases brake life.
Hybrids may have greater upfront costs, more complicated maintenance owing to multiple power systems, and a restricted all-electric range than electric vehicles.
A hybrid is more than just an electric vehicle. It mixes petrol and electric power sources, whereas electric automobiles depend solely on electricity for propulsion.
A hybrid automobile propulsion system combines petrol with an electric motor, allowing it to transition between the two power sources for greater fuel economy and decreased pollution.




